The Ionic Liquid System Market is rapidly evolving as a critical segment within the broader chemical and materials industry. Characterized by the unique properties of ionic liquid salts in a liquid state at relatively low temperatures, the market is witnessing robust growth driven by the increasing demand for sustainable, efficient, and innovative solutions across multiple industries. This comprehensive overview explores the market dynamics, key trends, segmentation, competitive landscape, and future outlook to present a thorough understanding of this transformative sector.
Market Overview and Size
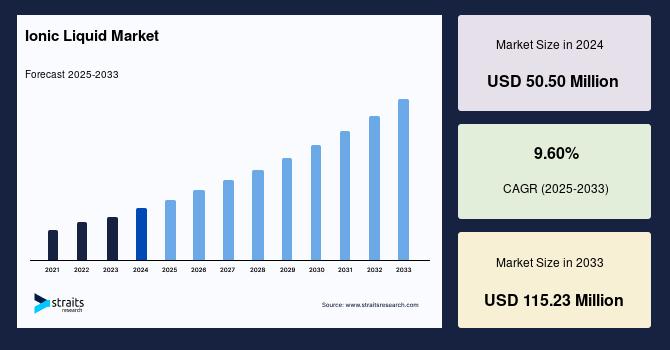
The Ionic liquid market size was valued at USD 50.50 million in 2024. It is estimated to reach an expected value from USD 55.35 million by 2025 to USD 86.20 million by 2033, registering a CAGR of 9.60% during the forecast period (2025-2033).
Understanding Ionic Liquids: Fundamentals and Properties
Ionic liquids are salts composed entirely of ions, which remain in a liquid state at temperatures below 100°C. Unlike traditional solvents, these liquids exhibit negligible vapor pressure, high thermal stability, non-flammability, and tunable solvation characteristics. These unique properties enable ionic liquids to replace volatile organic solvents (VOCs), thereby offering safer, environmentally friendly alternatives in various industrial processes.
Key properties that set ionic liquids apart include:
-
Low Volatility: Almost zero vapor pressure reduces emissions and fire hazards.
-
High Thermal and Chemical Stability: Suitable for high-temperature industrial processes.
-
Wide Electrochemical Window: Ideal for energy storage and electrochemical applications.
-
Solubility Tuning: By varying cation-anion combinations, ionic liquids can be tailored for specific solutes and reactions.
-
Biodegradability and Green Chemistry Alignment: Offering eco-friendly alternatives supporting sustainability goals.
Key Growth Drivers
1. Sustainability and Environmental Regulations
Global emphasis on green chemistry and environmental stewardship is a primary driver of ionic liquid adoption. Governments and industries worldwide are implementing stringent regulations to reduce harmful emissions and solvent waste. Ionic liquids, with their negligible vapor pressure and recyclable nature, serve as ideal substitutes for hazardous organic solvents in chemical synthesis, extraction, and industrial cleaning.
2. Expanding Industrial Applications
The versatility of ionic liquids extends across diverse industries:
-
Pharmaceuticals: Enhancing drug formulation and enabling green synthesis pathways.
-
Chemical Processing: Serving as solvents and catalysts in complex organic reactions.
-
Energy Storage: Facilitating safer and more efficient batteries, supercapacitors, and fuel cells.
-
Electroplating and Metal Processing: Providing uniform coatings with reduced environmental impact.
-
Biorefineries: Assisting in biomass dissolution and conversion to biofuels and biochemicals.
-
Plastics and Polymers: Acting as plasticizers, stabilizers, and additives to improve material properties.
This broad application spectrum continues to expand with ongoing research, driving market demand.
3. Technological Advancements and Innovation
Investments in research and development have yielded advanced ionic liquids tailored for specific uses. Innovations focus on:
-
Designing task-specific ionic liquids with enhanced selectivity and efficiency.
-
Improving scalability and cost-effectiveness of production processes.
-
Developing ionic liquids compatible with renewable energy technologies and green manufacturing.
These advancements reduce barriers to adoption and enhance the performance of industrial processes.
4. Growing Demand in Emerging Economies
Industrialization in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and parts of the Middle East & Africa is accelerating the demand for advanced chemical systems. The increasing adoption of ionic liquids in these regions is fueled by rising manufacturing capabilities, expanding pharmaceutical sectors, and enhanced environmental regulations.
Market Segmentation
By Application
-
Solvent and Catalyst Applications: Ionic liquids are extensively used as green solvents and catalysts, promoting environmentally benign chemical reactions with higher efficiency and yield.
-
Process and Operating Fluids: Utilized in heat transfer systems and lubrication where thermal stability and non-volatility are crucial.
-
Electrochemistry and Energy Storage: Ionic liquids serve as electrolytes in lithium-ion batteries, supercapacitors, and fuel cells, improving energy density and operational safety.
-
Plastics and Polymers: Enhance polymerization processes and improve the properties of plastics by acting as stabilizers and plasticizers.
-
Biorefineries: Facilitate the breakdown and processing of lignocellulosic biomass into biofuels and biochemicals.
By Region
-
Asia-Pacific: The largest market share holder, driven by industrial growth, expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing, and governmental push for sustainable technologies.
-
North America: Fastest growth rate, propelled by innovation hubs, extensive research activities, and strong regulatory support for green chemistry.
-
Europe: Robust market growth linked to stringent environmental laws and high consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
-
Latin America and Middle East & Africa: Emerging markets with growing industrial sectors and increasing environmental awareness, presenting significant future growth opportunities.
Competitive Landscape
The ionic liquid system market is marked by active participation from global chemical giants, specialized firms, and startups focused on innovation. Key market players include:
-
BASF SE: Pioneering sustainable ionic liquid solutions across multiple sectors.
-
Evonik Industries AG: Developing task-specific ionic liquids for pharmaceutical and chemical applications.
-
Merck KGaA: Offering ionic liquids with tailored properties for advanced electrochemical uses.
-
Solvionic SA: Specialized in high-purity ionic liquids for industrial and research applications.
-
Tatva Chintan Pharma Chem Pvt. Ltd.: Expanding presence in specialty ionic liquids for green chemistry.
-
Jinkai Chemical Co. Ltd.: Leading in Asian markets with diverse ionic liquid offerings.
-
Reinste Nanoventure: Innovating in energy storage and electrochemical ionic liquids.
-
Strem Chemicals Inc.: Supplying specialty chemicals including ionic liquids for research and industry.
These companies focus on product innovation, strategic collaborations, mergers, and geographic expansion to enhance their market position and address evolving customer needs.
Challenges in the Market
Despite promising growth, several challenges temper market expansion:
-
High Production Costs: The complex synthesis of ionic liquids currently results in higher prices compared to traditional solvents, limiting large-scale adoption.
-
Scalability Issues: Manufacturing ionic liquids at industrial scales remains challenging, requiring further technological breakthroughs.
-
Limited Awareness: Some industries lack comprehensive understanding of ionic liquids’ benefits, necessitating educational efforts.
-
Regulatory Hurdles: Diverse regulatory frameworks across countries can complicate market entry and product approval processes.
Addressing these challenges through innovation, economies of scale, and market education is critical for sustained growth.
Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
1. Development of Customized Ionic Liquids
Advances in molecular design allow the creation of task-specific ionic liquids tailored to precise industrial needs, enhancing efficiency and reducing waste.
2. Integration with Renewable Energy Systems
Ionic liquids are increasingly integral to next-generation energy storage technologies, including safer batteries and efficient fuel cells, aligning with global decarbonization goals.
3. Expansion into Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology
Enhanced solvent capabilities support green synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and bioprocessing, fostering sustainable healthcare manufacturing.
4. Growth of Sustainable and Circular Economy Practices
Ionic liquids’ recyclability and low environmental footprint align with circular economy principles, encouraging adoption by environmentally responsible enterprises.
5. Digitalization and Smart Manufacturing
Integration with Industry 4.0 and digital process control allows real-time monitoring and optimization of ionic liquid-based processes, improving productivity and reducing waste.
Conclusion
The ionic liquid system market is on an impressive growth trajectory, driven by increasing industrial demand, technological innovation, and a global push toward sustainable chemistry. Its unique combination of chemical and physical properties offers transformative benefits across multiple industries from pharmaceuticals and energy storage to plastics and biorefineries.
As production challenges are overcome and applications broaden, ionic liquids will become integral to the future of green chemistry and advanced manufacturing. With expanding research, strategic investments, and supportive regulatory environments, the ionic liquid system market is set to unlock significant economic and environmental value over the coming decade.