The Waste Heat Recovery (WHR) market is gaining rapid momentum as industries across the globe intensify efforts to improve energy efficiency, reduce carbon emissions, and embrace sustainable production models. In an era where energy conservation has become not only an economic imperative but also a regulatory and environmental necessity, WHR systems offer a solution that aligns with global trends in decarbonization, cost reduction, and operational excellence.
From heavy industries like cement and steel to power generation, chemicals, and oil and gas, waste heat recovery technologies are being integrated into core infrastructure to harness thermal energy that would otherwise be lost. This recaptured energy is then converted into usable power, steam, or process heat—creating a closed-loop system of efficiency and environmental responsibility.
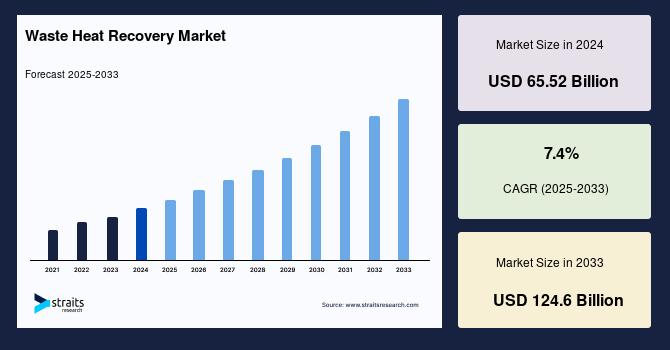
Market Size and Growth Overview
The global waste heat recovery market size was valued at USD 65.52 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach from USD 70.37 billion in 2025 to USD 107.9 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.4% during the forecast period (2025-2033).
This robust expansion reflects increasing investment in clean energy technologies, rising energy costs, industrial expansion in emerging economies, and tightening environmental regulations across major markets.
What is Waste Heat Recovery?
Waste Heat Recovery refers to the process of capturing heat generated as a by-product of industrial processes—heat that would otherwise be released into the environment—and reusing it for other applications. The recovered heat can be utilized for:
-
Electricity generation
-
Steam or hot water production
-
Pre-heating combustion air or materials
-
District heating systems
-
Industrial drying or cooling operations
By installing WHR systems, companies can significantly reduce their fuel consumption, energy costs, and emissions—while improving process efficiency and competitiveness.
Key Market Drivers
1. Rising Energy Prices and Industrial Costs
Energy-intensive industries are under constant pressure to reduce operational costs. WHR technologies provide an attractive return on investment by converting waste heat into usable energy, thus lowering energy bills and reducing dependency on external sources.
2. Government Regulations and Emission Standards
Governments around the world are implementing stricter environmental regulations, including carbon taxes and emission caps. WHR solutions help industries meet these requirements while earning incentives, tax credits, or carbon offsets.
3. Push Toward Carbon Neutrality
As more companies pledge net-zero emission goals, WHR becomes a strategic lever in their decarbonization roadmap. It’s a practical solution to reduce Scope 1 emissions directly tied to industrial operations.
4. Technological Advancements
Innovations in heat exchangers, Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) systems, and data-driven monitoring have enhanced the efficiency, compactness, and scalability of WHR systems—making them more accessible to small and medium enterprises, not just large conglomerates.
5. Growth of Industrial Sectors
Rapid urbanization and industrialization—especially in emerging economies across Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America—are increasing the volume of industrial waste heat, creating fertile ground for WHR market expansion.
Market Segmentation
By Application
-
Electricity Generation: Capturing high-grade waste heat to generate electricity via steam turbines or ORC units. This is the fastest-growing segment, especially in the cement, glass, and power industries.
-
Pre-heating and Drying: Used to heat combustion air or materials before processing, improving combustion efficiency and reducing fuel usage.
-
Steam and Hot Water Production: Widely adopted in food & beverage, pulp & paper, and textile industries.
-
District Heating: Some industrial WHR systems feed into municipal heating networks, providing a secondary revenue stream.
By Technology
-
Recuperators
-
Regenerators
-
Heat Pipe Exchangers
-
Waste Heat Boilers
-
Thermoelectric Generators
-
Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC)
ORC systems are gaining popularity due to their ability to convert low- to medium-grade waste heat into electricity—offering flexibility across industries.
By End-Use Industry
-
Cement
-
Iron & Steel
-
Petrochemicals and Refining
-
Power Generation
-
Glass
-
Food Processing
-
Pulp and Paper
Among these, cement and steel industries dominate due to their high thermal energy intensity, while oil & gas is increasingly investing in WHR to improve refinery energy efficiency.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America, particularly the United States, leads in WHR adoption due to a mature industrial base, strict environmental policies, and advanced technological integration. The presence of leading manufacturers and research institutions further accelerates innovation and deployment.
Europe
Europe has been a pioneer in energy recovery systems. With ambitious climate targets and robust funding for clean technologies, countries like Germany, France, and the Nordic nations are aggressively expanding WHR infrastructure.
Asia-Pacific
This is the fastest-growing regional market, driven by massive industrialization in countries such as China, India, Indonesia, and Vietnam. Government support for energy-efficient technologies and rising energy demand are key growth catalysts.
Middle East and Africa
Though still emerging, the MEA region is beginning to embrace WHR in sectors like oil refining and power generation as part of broader efforts to improve energy sustainability and reduce fossil fuel dependency.
Key Benefits of WHR Implementation
-
Reduces energy consumption by up to 30%
-
Cuts carbon dioxide emissions significantly
-
Lowers operational and fuel costs
-
Extends equipment life by reducing thermal stress
-
Increases system reliability and resilience
-
Enhances corporate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) profile
Challenges to Market Growth
High Initial Investment
While long-term benefits are significant, upfront costs for system design, customization, and installation can be high—particularly for small and medium enterprises.
Integration Complexities
Retrofit projects, especially in aging infrastructure, may face engineering challenges. Proper integration with existing systems requires detailed energy audits and skilled expertise.
Lack of Awareness
Many businesses, particularly in developing regions, are still unaware of WHR benefits or are skeptical about ROI timelines.
Variability in Heat Sources
Not all waste heat is equal. The quality and consistency of available heat impact the efficiency of recovery systems.
Emerging Trends and Future Outlook
Digitalization of WHR Systems
Smart sensors, IoT integration, and AI-powered analytics are enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and system optimization, making WHR more efficient and easier to manage.
Micro-WHR Systems for SMEs
Modular and compact WHR units are being developed for smaller-scale operations, opening up a new segment of untapped market potential.
Hybrid Energy Systems
Combining WHR with solar thermal or biomass systems creates hybrid setups that optimize energy efficiency and reduce fossil fuel use.
Energy-as-a-Service (EaaS) Models
To overcome capital barriers, new business models allow third-party investors to finance WHR systems in return for shared savings, making the technology accessible to more businesses.
Competitive Landscape
The market is moderately consolidated, with key players investing in R&D, product innovation, and strategic partnerships. Major companies operating in the WHR market include:
-
Global engineering firms providing turnkey WHR solutions
-
Industrial boiler and heat exchanger manufacturers
-
Emerging startups specializing in compact ORC technology
-
Energy services companies (ESCOs) facilitating financing and implementation
Innovation, customization, and lifecycle support are becoming key differentiators.
Conclusion
The Waste Heat Recovery market is poised for sustained growth as industries worldwide push toward energy efficiency, cost reduction, and decarbonization. By turning industrial by-product heat into valuable energy, WHR technologies not only support bottom-line savings but also align with the global sustainability agenda.
As innovation lowers costs and boosts scalability, WHR systems are no longer just an option for large-scale factories but are becoming an essential tool for every energy-conscious business. With the right investment, policy support, and education, WHR has the potential to reshape industrial energy use for a cleaner, more efficient future.