Executive Summary
The global Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) market is experiencing significant expansion, driven by its exceptional performance properties and its growing use across high-growth sectors such as electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy, chemical processing, electronics, and construction. With rising demand for high-performance polymers that can withstand harsh environments, PVDF has emerged as a critical material in various industrial applications.
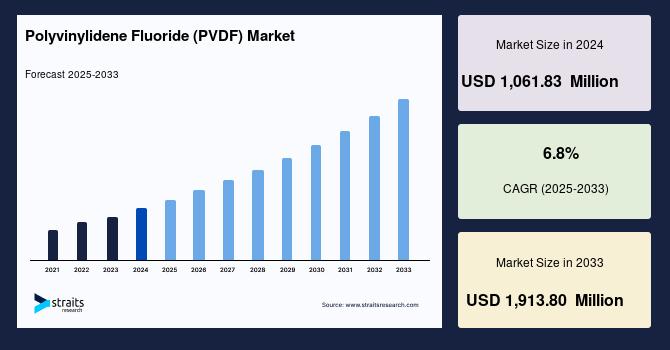
The global polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) market size was valued at USD 1,061.83 million in 2024 and is projected to reach from USD 1,128.2 million in 2025 to USD 1,913.80 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.8% during the forecast period (2025-2033).
What is Polyvinylidene Fluoride?
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) is a highly non-reactive thermoplastic fluoropolymer. Known for its excellent chemical resistance, high thermal stability, mechanical strength, UV resistance, and low permeability to liquids and gases, PVDF is used in applications where other plastics fail due to environmental conditions. It is commonly supplied in the form of pellets, sheets, tubes, and coatings.
PVDF is utilized both in pure polymer form and in composite blends for applications requiring electrical insulation, resistance to solvents and corrosives, and flame retardancy.
Market Drivers
1. Rapid Growth of Electric Vehicles and Lithium-Ion Batteries
One of the most significant factors driving PVDF demand is its application as a binder material in lithium-ion batteries, especially in the cathode and anode electrodes. PVDF binders improve battery performance by offering high chemical stability and excellent adhesion properties, making them indispensable in EV batteries.
As the global automotive industry continues its shift toward electric mobility, the demand for lithium-ion batteries and consequently, PVDF is surging.
2. Rising Demand in the Chemical Processing Industry
PVDF’s strong resistance to acids, bases, and solvents makes it an ideal material for pipes, valves, tanks, pumps, and fittings used in aggressive chemical environments. Industries dealing with petrochemicals, acids, and corrosive materials increasingly rely on PVDF for reliable fluid handling systems.
3. Expanding Applications in Construction and Architecture
PVDF-based coatings are extensively used in construction materials such as aluminum composite panels, roofing systems, and cladding. These coatings offer superior weather resistance, UV stability, and color retention, making them popular in high-end architectural applications. As urbanization and infrastructure investments grow worldwide, demand for PVDF-coated building materials is increasing.
4. Technological Advancements in Membranes and Water Filtration
PVDF is used in the manufacture of ultrafiltration (UF) and microfiltration (MF) membranes for water purification systems. Its hydrophobicity and excellent membrane-forming characteristics make it a preferred polymer in the filtration industry. Rising concerns over water scarcity and the need for clean water solutions are fueling demand for PVDF-based filtration systems.
Key Market Segments
By Application
-
Wires and Semiconductors: Used in insulation and jacketing of wires due to high dielectric strength and flame retardancy.
-
Pipes and Fittings: Ideal for harsh chemical transfer systems.
-
Films and Sheets: Utilized in electronics, solar panels, and packaging.
-
Coatings: Applied in construction, automotive, and aerospace components.
-
Membranes: Critical in filtration systems for industrial and municipal water treatment.
-
Lithium-Ion Batteries: Fastest-growing segment due to the EV boom.
By End-Use Industry
-
Electrical and Electronics: PVDF films are used in capacitors, cable insulation, and photovoltaic back sheets.
-
Chemical Processing: Valued for corrosion-resistant piping and vessels.
-
Automotive and Transportation: Growing demand in fuel systems and batteries.
-
Aerospace and Defense: Lightweight and durable materials for insulation and fluid systems.
-
Construction: Use in PVDF-based coatings for long-lasting facades and roofs.
-
Others: Healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and marine industries.
Regional Outlook
North America
North America accounts for a significant share of the global PVDF market, supported by strong industrial infrastructure, growing investment in battery production, and advancements in chemical processing. The United States leads the region with major manufacturers investing in expanding their domestic PVDF capacities, especially for battery-grade materials.
Europe
Europe is witnessing robust growth in the PVDF market due to stringent environmental regulations, a strong automotive base, and growing investments in clean energy and sustainable construction. Countries like Germany, France, and the Netherlands are expanding their EV infrastructure, which in turn drives battery and PVDF demand.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the largest and fastest-growing region for PVDF. China, Japan, South Korea, and India are key markets, driven by:
-
Massive electronics manufacturing bases
-
Expanding EV production
-
Growth in water treatment facilities
-
Rapid urbanization and infrastructure development
China dominates the region in both production and consumption, with local companies expanding capacity to reduce reliance on imports.
Latin America and the Middle East & Africa
These regions are in the early stages of PVDF adoption but show growing potential due to increasing investments in water treatment, chemical manufacturing, and energy storage systems. Brazil, Mexico, South Africa, and the UAE are notable emerging markets.
Market Trends
1. Shift Toward Sustainable PVDF Production
With global emphasis on sustainability, manufacturers are exploring greener production methods for PVDF, including renewable feedstocks and recycling of fluorinated polymers. Environmental compliance and lifecycle assessments are becoming key to market entry.
2. Integration in 3D Printing and Advanced Manufacturing
Innovators are exploring PVDF in additive manufacturing for high-performance parts. Its lightweight, heat resistance, and mechanical strength make it suitable for aerospace and medical applications.
3. Consolidation and Capacity Expansion
Major chemical companies are investing in new plants and capacity expansions to meet global PVDF demand. Strategic acquisitions and long-term supply agreements are shaping the competitive landscape.
Competitive Landscape
The global PVDF market is moderately consolidated, with a mix of multinational giants and regional players. Key market participants focus on:
-
Enhancing product purity for battery applications
-
Innovating new grades for coatings and films
-
Strengthening supply chains for global distribution
Leading Companies
-
Arkema SA
-
Solvay S.A.
-
3M Company
-
Kureha Corporation
-
Daikin Industries Ltd.
-
Dongyue Group
-
Shanghai Ofluorine Chemical Technology Co. Ltd.
-
Quadrant Engineering Plastics
-
RTP Company
-
SABIC
These players are investing in R&D to develop application-specific PVDF grades and forming partnerships with battery manufacturers, automotive OEMs, and filtration companies.
Market Challenges
1. High Cost of Production
PVDF is more expensive compared to other thermoplastics, which limits its adoption in price-sensitive applications.
2. Supply Chain Disruptions
Dependence on specific raw materials and limited production capacities in some regions can result in supply shortages and price volatility.
3. Environmental and Regulatory Barriers
As a fluoropolymer, PVDF faces scrutiny under evolving environmental regulations related to fluorinated compounds. Manufacturers must address sustainability concerns and ensure compliance with chemical safety standards.
Future Outlook
The PVDF market is poised for strong and sustained growth. Its role in supporting next-generation technologies like electric vehicles, renewable energy, advanced filtration, and smart infrastructure positions it as a material of the future. Continued R&D investment, process optimization, and regulatory alignment will be key in unlocking the full potential of PVDF in global markets.
Conclusion
Polyvinylidene Fluoride is more than just a high-performance plastic it's a cornerstone material in many transformative technologies shaping the modern world. From the electric vehicle revolution to next-gen water purification systems, PVDF's versatility, durability, and functional superiority ensure that its global demand will only accelerate in the years ahead. As industries look for reliable, high-value materials that perform under pressure, PVDF will remain at the forefront of innovation and industrial resilience.